Vitiligo is a chronic skin condition characterized by the loss of pigmentation, leading to the development of white patches on the skin. These depigmented patches are caused by the destruction or malfunction of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color.
Melanocytes are specialized cells located in the skin, hair follicles, eyes, and other tissues, and their primary role is to produce melanin. This pigment gives skin, hair, and eyes their color. In vitiligo, these melanocytes are lost or damaged, resulting in the characteristic white or light-colored patches of skin.
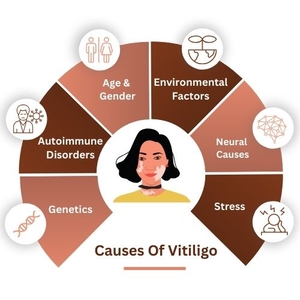
The exact cause of vitiligo is not completely understood, but several factors contribute to its development:
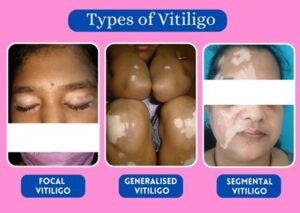
Conditions like Pityriasis Alba, Tinea Versicolor, and Post-Inflammatory Hypopigmentation may appear similar to vitiligo, but they differ in their causes and symptoms.
While vitiligo cannot always be prevented, using sunscreen to protect depigmented skin from sunburn and minimizing tanning can help reduce contrast between affected and unaffected skin. Cosmetics like makeup and self-tanning lotions can also be used to cover the patches.

Homeopathic remedies focus on stimulating the functioning of melanocytes to restore normal skin color. Some of the most commonly used homeopathic treatments for vitiligo include:
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to vitiligo treatment, addressing both the physical and emotional aspects of the condition. While modern medicine focuses primarily on managing vitiligo with immunosuppressive treatments, homeopathy aims to restore normal pigmentation by stimulating melanocyte function, often without the side effects associated with conventional treatments.
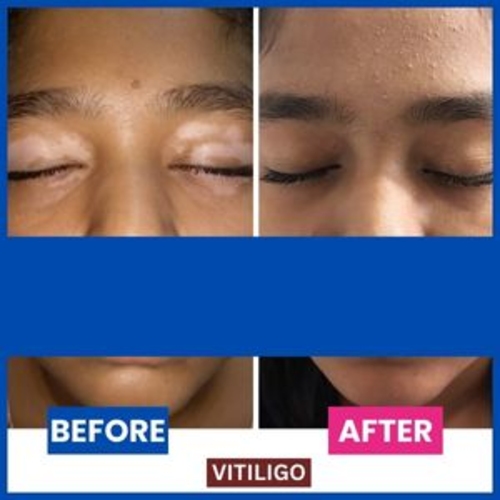
Many patients have reported significant improvements in their vitiligo condition through homeopathic treatment. For example, a young girl in Mumbai saw her white patches regain their original color within two years, and a 17-year-old woman experienced complete resolution of her vitiligo after a year of homeopathic care.


Vitiligo can appear at any age, but it often first manifests between 20 and 30 years.
No, Vitiligo is non-contagious.
Focal and segmental patterns usually do not spread, while the generalized pattern can be unpredictable and may randomly stop.
Triggers can include autoimmune disorders, genetic factors, skin trauma, and exposure to chemicals, sunburn, emotional distress, and heredity.
Diagnosis may involve medical screenings, including family history, skin trauma assessment, premature graying of hair, stress, or physical illness. Eye examinations and blood tests may also be conducted.